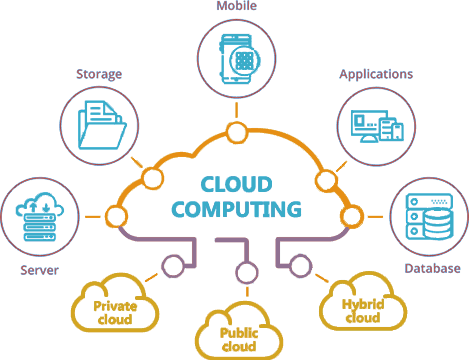
Cloud computing is a term that has made its way into everyday business IT discussions. An appropriate cloud computing strategy that fits your day-to-day operations, as well as long-term usability, can be an essential component of business success. Cloud computing gives unprecedented access and options to businesses of all sizes. Before you make the move, take a moment to understand the different types of cloud computing available. This will better prepare you to decide which cloud environment is better suited to your needs. The cloud environment that works for a local office with 10 employees is probably not ideal for a law firm with locations across the country. The three types of cloud computing are public, private and hybrid.
- Public Cloud
Public cloud computing is more familiar because most people use it daily. The public cloud is provided as a service over the Internet. With this option, your business is not responsible for maintaining any technology or infrastructure – the service provider does it all. Servers and other infrastructure are kept off-site. In fact, it's unlikely you'll ever come face-to-face with the infrastructure you use daily.
The public cloud is generally the least expensive option, but those cost savings can be the detriment to your organization’s needs. For example, if your organization uses cloud-enabled applications, the public cloud is an excellent solution. However, if you use applications that are not compatible with the cloud, you’ll require some form of on-site infrastructure for support.
A public cloud infrastructure, and in some cases a hybrid cloud, creates an environment that is easily managed. Everything from servers and software to apps and mobile devices are connected to a public or hybrid cloud and can easily be managed remotely from any location. Network administrators can manage all facets of a public cloud without having to make office visits or travel to different sites. Every device and program accessing the network is capable of remote management.
There are two reasons this is easiest in a public cloud environment: centralized control and shared resources. As mentioned, public clouds are managed from a centralized location rather than multiple office sites. When a software program is ready to update or a piece of hardware needs to be upgraded, it can be done quickly in that one location and impacts everyone using the network. Also, because resources are shared in a public cloud, all parties using the network share the costs of implementing any changes.
Scalability is important for many companies. Whether the company itself is growing in terms of employees or the number of services offered, the need to accommodate changes in bandwidth, capacity and operability is most easily met in a public or hybrid cloud environment. The public cloud is simple to navigate, and no resources need to be devoted to managing any infrastructure. While you share the infrastructure with other businesses (hence the cost savings), you can still scale your services up or down as you need them.
Public clouds have the lowest cost, on average, for implementation. Because the services and hardware are shared by multiple users, there is not a need for a local data center. This significantly reduces the cost of purchasing equipment, software licenses and operating the network for all users.
- Private Cloud
The private cloud is also referred to as an internal cloud or an enterprise cloud. The primary difference between a private cloud and a public cloud is that the private cloud is a service that's deployed over an internal network. This means you own the infrastructure, which may be located on-site or in a data center, and resources are required to manage and maintain your equipment. Private clouds provide the highest security available in a cloud environment, limiting your business's exposure to risks. They only run applications and hardware designed for your organization’s access. In terms of security software, you can implement the best solution to match the security requirements of your firm. Since your employees are the only ones accessing the network through your cloud data center, security can be much higher than what can be achieved in a public cloud.
Private clouds also offer more flexibility in terms of capabilities than their public counterparts. These enhancements come at a cost, causing private clouds to cost more than public environments.
Your organization will enjoy the strongest network performance with the adoption of a private cloud. The infrastructure that supports a private cloud data center is deployed solely for use by your organization. Whether it is managed internally by your IT department or handled by a third-party IT firm, the environment is for your company’s use alone, which allows the network infrastructure to be designed to directly meet your needs.
In some cases, private clouds can provide lower implementation costs compared to establishing an entirely separate wide area network (WAN) infrastructure. In particular, Platform as a Service (PaaS) options are much more affordable for enterprises that want to offer employees access to proprietary applications from branch offices.
- Hybrid Cloud
As the name implies, a hybrid cloud combines some of the features of both public and private clouds. A hybrid cloud attempts to utilize the individual strengths of each type of cloud computing while avoiding the weaknesses. A hybrid cloud can be custom designed to meet your organization’s specific needs.
A hybrid cloud gives you the benefits of both private and public cloud environments. This means that with a hybrid cloud you have the most options available to your business. One disadvantage of hybrid clouds is that they can create a more complex computing infrastructure, which may take more time to set up and manage, versus a public or private cloud.
Whether your business operates on a public, private or hybrid platform, updating software programs on the network and applying the latest security patches is a breeze. A network administrator can log onto the system and apply fixes and upgrades. These updates will take effect immediately on connected devices (mobile devices not connected at the time a change occurs will be updated the next time they connect to the cloud).
Hybrid environments can be created with high security as well. You save money by accessing Software as a Service (SaaS) applications on a public cloud network. To ensure proper security measures are in place, you establish a private cloud inside your firewall that provides a virtual private network (VPN), allowing your organization’s security software to be managed separately from the public cloud environment.
Public VS. Private VS. Hybrid Clouds
Ultimately, you must consider your organization's unique needs when deciding between the different types of cloud computing. Think about what types of tasks you need to be accomplished daily, the software applications you require and how you want to fund your technology. By doing this upfront research, you'll be able to choose the type of cloud computing that's best suited to how you do business.
Tri-Copy is here to help you decide what type of cloud is best for your business needs. Give us a call to set up your free consultation today.